Understanding the Basics of Shipping
Shipping plays a crucial role in the global economy by facilitating the movement of goods and commodities across vast distances. At its core, shipping involves the transportation of products from one location to another, typically through various methods such as air freight, sea freight, and ground transportation. Each method has distinct advantages and is chosen based on factors such as cost, speed, and the nature of the goods being transported.
Air freight is known for its speed and efficiency, making it ideal for transporting high-value or time-sensitive goods. Sea freight, on the other hand, is cost-effective for large volumes of goods, especially over long distances, although it generally takes longer than air transport. Ground transportation, which includes trucking and rail services, is often used for regional deliveries and is essential for the final leg of many shipping journeys.
The shipping process involves several key players. Carriers are responsible for the actual transportation of goods, whether by air, sea, or land. Shippers, typically the owners of the goods, arrange for their transportation, while freight forwarders act as intermediaries, coordinating the logistics and ensuring that shipments move smoothly from origin to destination.
Shipping is indispensable in the global economy as it enables trade and commerce by connecting producers with consumers worldwide. It allows nations to access products not available locally and supports economic growth by enabling businesses to reach international markets.
In the shipping industry, various terms and acronyms are commonly used. For instance, FOB (Free on Board) indicates that the seller delivers goods on board a vessel chosen by the buyer, while CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) means the seller covers these costs to a specified destination port. DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) signifies that the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the buyer's location and paying all associated duties and taxes.
The shipping industry is regulated by numerous bodies and international agreements to ensure safety, security, and environmental protection. Organizations such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the International Air Transport Association (IATA) set standards and guidelines that govern shipping practices globally, fostering a more efficient and secure trade environment.










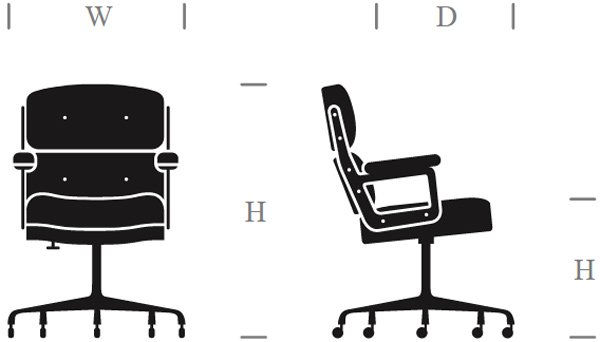
































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.